Page Contents
ToggleMuscle loss prevention is crucial for maintaining strength and independence as you age. Have you noticed climbing stairs feels harder than it used to? Maybe lifting groceries seems more challenging, or you feel less steady on your feet? If you’re in your 40s, 50s, or beyond, you might be experiencing the early signs of sarcopenia – a condition that affects millions of North Americans but often goes unrecognized until it significantly impacts daily life.
Sarcopenia is the age-related progressive loss of muscle mass and strength that naturally begins in your 30s or 40s but accelerates dramatically after age 65. One reason for this decline is reduced mitochondrial activity — which is why supplements like Mitolyn that support cellular energy production and muscle preservation can be especially helpful during this stage of life. Similarly, Joint Genesis targets joint health directly, with ingredients that aim to ease age-related inflammation and promote flexibility.
For women in midlife, hormonal changes during menopause can further accelerate muscle loss — exploring natural solutions like MenoRescue may help address both muscle health and hormonal balance.
While this might sound like an inevitable part of aging, the truth is far more empowering: with the right knowledge and approach, you can take meaningful action to maintain your strength, independence, and quality of life for decades to come.
Understanding Sarcopenia: More Than Just Getting Older
The medical definition of sarcopenia goes beyond simple aging. It’s the gradual loss of muscle mass, strength, and function that occurs when your body stops producing adequate proteins needed for muscle growth and maintenance. As muscle cells shrink and decrease in number, your muscles literally begin to thin – a process called muscle atrophy.
What makes sarcopenia particularly concerning is its cascading effects. Beyond the obvious challenge of feeling weaker, this condition significantly increases your risk of falls, fractures, and loss of independence. It affects your musculoskeletal system and becomes a major factor in increased frailty, potentially leading to hospitalizations and the need for long-term care.
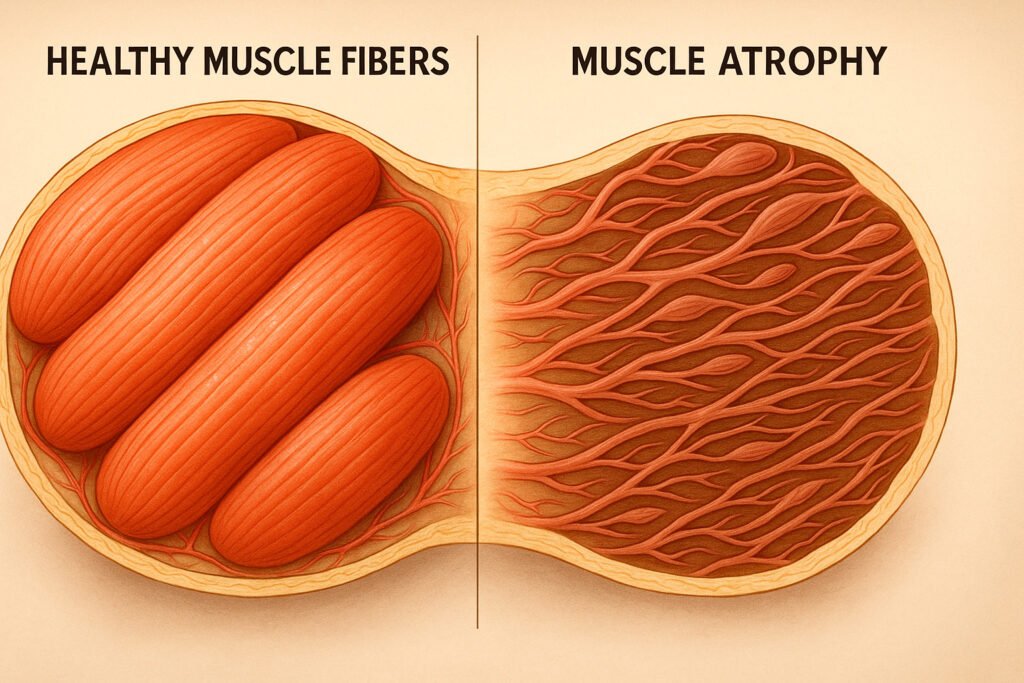
The statistics are sobering: sarcopenia affects 5% to 13% of people ages 60 and older, jumping to 11% to 50% of those over 80. However, many cases go undiagnosed, meaning these numbers likely represent only the tip of the iceberg.
Recognizing the Warning Signs of Muscle Weakness
The most common symptom of sarcopenia is muscle weakness, but the condition presents itself in various ways that might seem like normal aging:
- Difficulty climbing stairs or rising from chairs
- Reduced grip strength when opening jars or carrying bags
- Unexplained weight loss, particularly muscle mass
- Frequent falls or feeling unsteady
- Decreased endurance during daily activities
- Loss of physical performance in tasks you once found easy
These symptoms often develop gradually, which is why many people don’t realize they’re experiencing sarcopenia until it has progressed significantly.
Why Does Muscle Atrophy Happen?
While aging is the primary driver of sarcopenia, several factors contribute to accelerated muscle loss:
- Hormonal Changes: As you age, your body produces less testosterone and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), both crucial for maintaining muscle mass and strength.
- Protein Production Decline: Your body becomes less efficient at producing the proteins your muscles need to grow and repair themselves.
- Lifestyle Factors: Physical inactivity, poor nutrition, chronic diseases, and certain medications can all accelerate muscle loss.
- Inflammatory Processes: Chronic low-grade inflammation, common as we age, can interfere with muscle protein synthesis. Since inflammation often affects both muscles and joints, you may also want to explore natural solutions like Joint Genesis, which is designed to ease stiffness and improve range of motion.
The process typically begins subtly in your 30s or 40s, with muscle mass declining by about 3-8% per decade. However, this rate accelerates significantly between ages 65 and 80, when you might lose as much as 8% of your muscle mass each decade.
Natural Approaches to Build Muscle Mass Through Muscle Loss Prevention
The encouraging news about sarcopenia is that lifestyle modifications can effectively treat and even reverse its effects. Here are evidence-based strategies that align with natural health principles and help you build muscle mass:
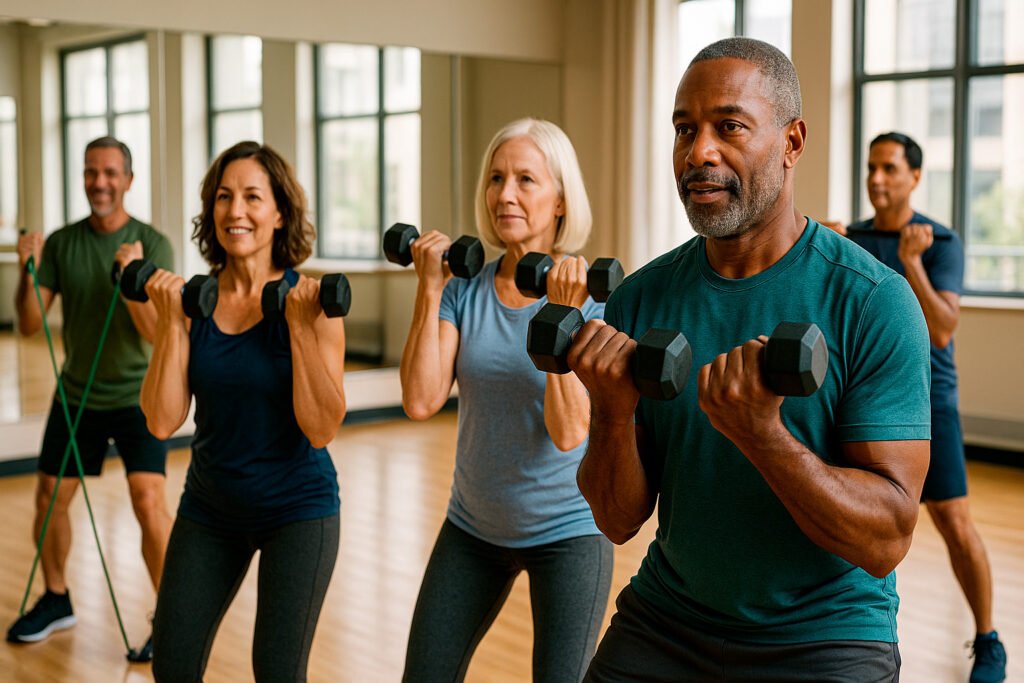

- Resistance Training: Progressive resistance exercises are the gold standard for combating sarcopenia. This doesn’t necessarily mean lifting heavy weights at a gym – resistance bands, bodyweight exercises, and functional movements can all be effective. The key is challenging your muscles progressively over time.
- Protein Optimization: Adequate protein intake becomes increasingly crucial as you age. Focus on high-quality protein sources distributed throughout the day, as your body becomes less efficient at processing large amounts of protein in single meals.
Movement Integration: Beyond formal exercise, incorporating more movement into daily life helps maintain muscle function. Take stairs instead of elevators, park farther away, or engage in active hobbies like gardening or dancing.
- Balance and Flexibility Work: Activities like yoga, tai chi, or simple balance exercises help maintain the functional strength needed for daily activities while reducing fall risk.
Nutritional Strategies for Muscle Health
Supporting muscle health through nutrition involves more than just protein, though adequate protein intake remains crucial:
- Timing Matters: Distributing protein intake throughout the day – approximately 25-30 grams per meal – optimizes muscle protein synthesis better than consuming large amounts in single meals.
- Quality Sources: Focus on complete proteins containing all essential amino acids: lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based combinations.
- Supporting Nutrients: Vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants all play roles in muscle health and recovery.
- Hydration: Proper hydration supports muscle function and recovery, becoming increasingly important as kidney function may decline with age.

The Mind-Body Connection in Muscle Preservation
Your mental health and stress levels significantly impact muscle health. Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can accelerate muscle breakdown. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or enjoyable social activities can support your physical efforts to maintain muscle mass.
Sleep quality also plays a crucial role, as muscle repair and growth hormone production occur primarily during deep sleep phases.
Taking Action: Your Sarcopenia Prevention Plan
The most effective approach to preventing or reversing sarcopenia combines multiple strategies:
- Start Where You Are: If you’re currently sedentary, begin with gentle movements and gradually increase intensity. If you’re already active, consider adding specific resistance training.
- Consistency Over Intensity: Regular, moderate activity proves more beneficial than sporadic intense efforts.
- Professional Guidance: Consider working with healthcare providers familiar with age-related muscle loss, particularly if you have existing health conditions.
- Monitor Progress: Track functional improvements like climbing stairs more easily or improved balance, not just weight or appearance.
- Community Support: Engaging in group activities or classes can provide motivation and social connection, both important for long-term success.
Looking Forward: Maintaining Independence and Vitality
Sarcopenia doesn’t have to be an inevitable part of aging. While you cannot completely prevent age-related changes, you have significant control over the rate and extent of muscle loss. The strategies outlined here – resistance training, optimal nutrition, stress management, and consistent movement – form a comprehensive approach that can help you maintain strength, independence, and quality of life well into your later years.
Remember, it’s never too early or too late to start. Whether you’re in your 40s looking to prevent future problems or in your 70s wanting to regain lost strength, your muscles retain the remarkable ability to respond to proper stimulation and care.

The journey toward maintaining muscle health is not just about preventing a medical condition – it’s about preserving your ability to live life on your terms, maintaining the strength to enjoy activities you love, and keeping the independence that allows you to thrive in your golden years.
For many, supporting joint health is just as crucial as maintaining muscle strength. Joint Genesis offers a natural way to promote flexibility and comfort, making it easier to stay active and independent as you age.
Sources
This article was inspired by and adapted to better serve the readers of Best Natural Health Products from “Sarcopenia (Muscle Loss): Symptoms & Causes”. Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23167-sarcopenia. Accessed on: June 30, 2025.
Mark Henderson is the Lead Product Analyst and resident skeptic. He specializes in the "Dosage Audit," rigorously cross-referencing label claims against clinical trials to expose underdosed products. Mark helps readers bypass the hype to find longevity solutions with a proven ROI.
- Mark Henderson
